This tutorial is outdated. We're currently working on an updated version. In the meantime, for instructions on building a chat app using CometChat, please visit our documentation.
App and web development have come a long way over the last few years. We use a lot of social applications, and chat applications every day, including Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, WhatsApp, and so on. One of the most widely used features is live chat. Using the CometChat React Native UI Kit, React Native, and Firebase, you will learn how to build one of the Instagram clone with minimal effort. This tutorial will help you to create the Instagram clone in React Native, Firebase, and CometChat.
We should cover the following topics in this tutorial:
Authentication
A way for users to log in and register
Login the logged-in user to CometChat
Add API call when a user registers so that the user is created in CometChat
User superhero dummy users for this tutorial
User Profiles
A tab to display user details.
Display all posts made by the user.
Follow Requests
Users can follow other users by simply clicking a ‘Follow’ button on any users profile
Create New Post
Functionality to upload new image/video as post
Feed
A tab where users can see content uploaded by other users they follow
Functionality to Like posts
Reels
Ability for users to upload short (1-min) videos
Display these reels in the Feeds tab
Notifications
Notifications for new messages, likes and follow requests
A tab where users can see all the latest notifications.
Chat
Ability to text all other users
Voice & Video calling
Reactions, Media sharing, and read receipts
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, you must have a degree of understanding of the general use of React Native. This will help you to improve your understanding of this tutorial.
Installing the App Dependencies
You need to have Node.js installed on your machine.
Create a new project with the name instagram-clone with version 0.63.3 by running the following statement.
Copy the dependencies from here and run the following statement.
Run cd to the iOS folder then run pod install to install the pods. Once pods are installed run cd to go back to the root folder.
Configuring CometChat SDK
Create your CometChat account.
Add real-time chat with minimal effort using CometChat
After registering a new account, you need to the log in to the CometChat dashboard.
Log in to the CometChat Dashboard with your created account. From the dashboard, add a new app called "instagram-clone".
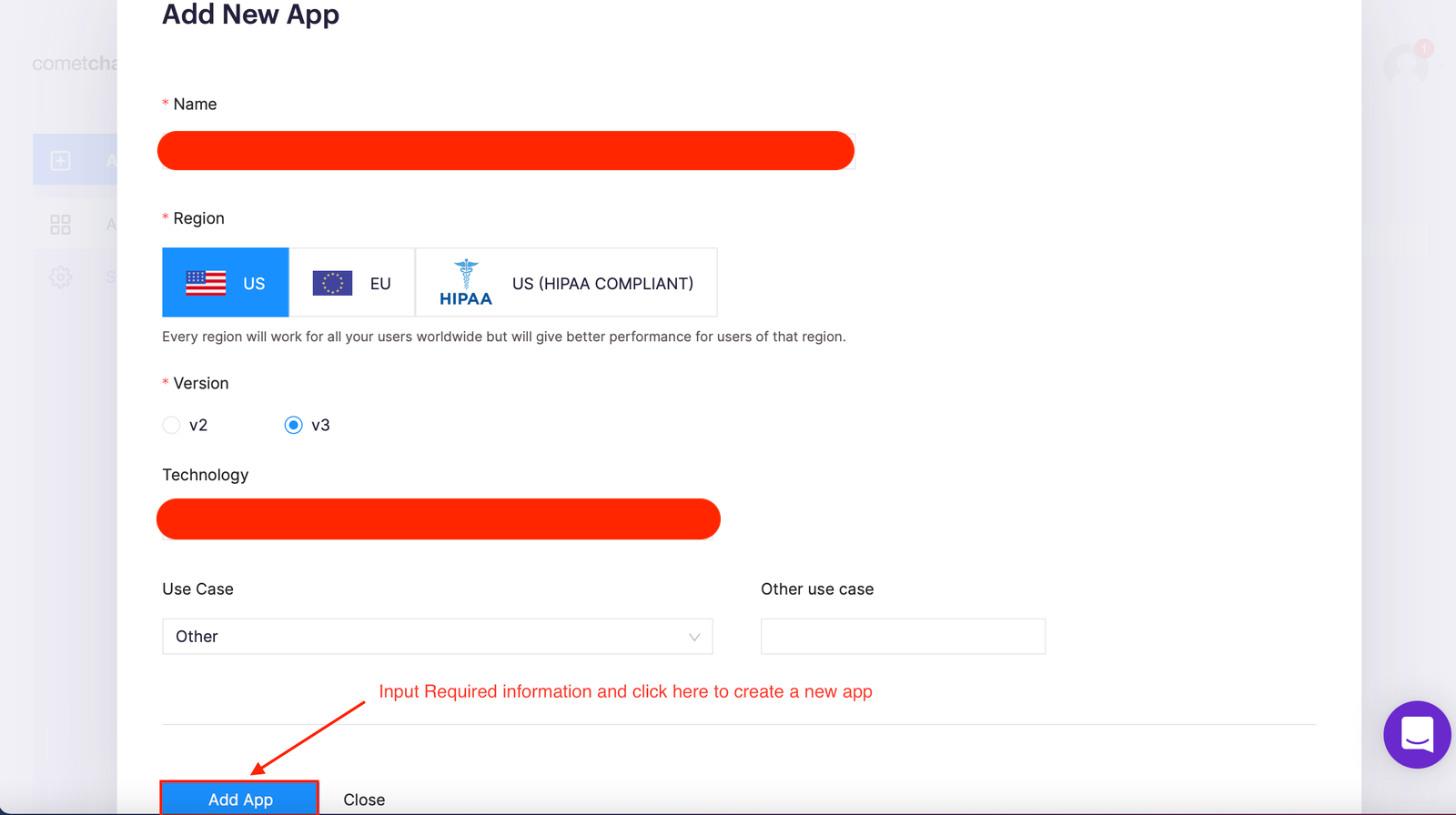
Create a new CometChat app - Step
Select this newly added app from the list.
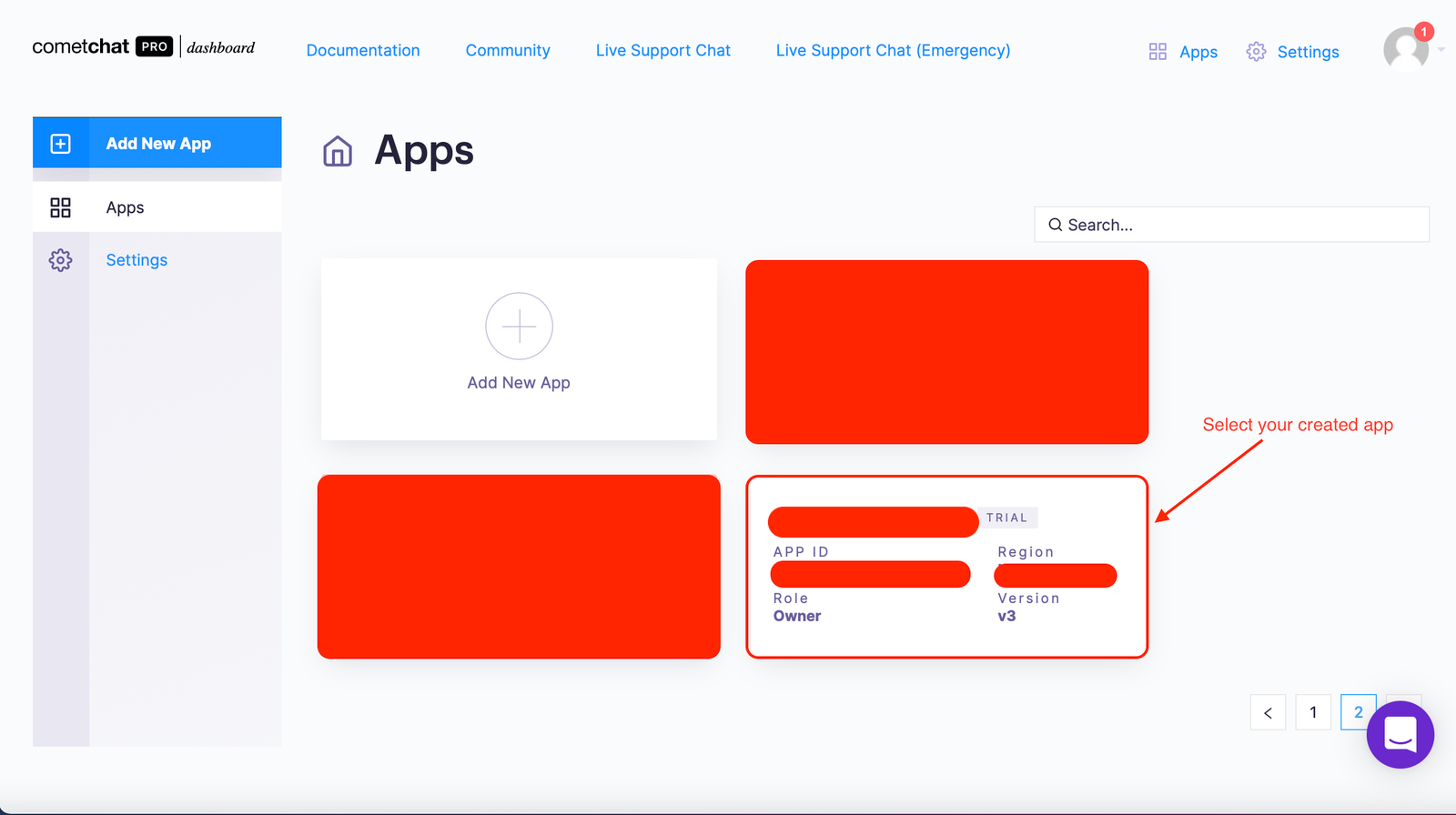
Select your created app
From the Quick Start copy the APP_ID, REGION, and AUTH_KEY, which will be used later.
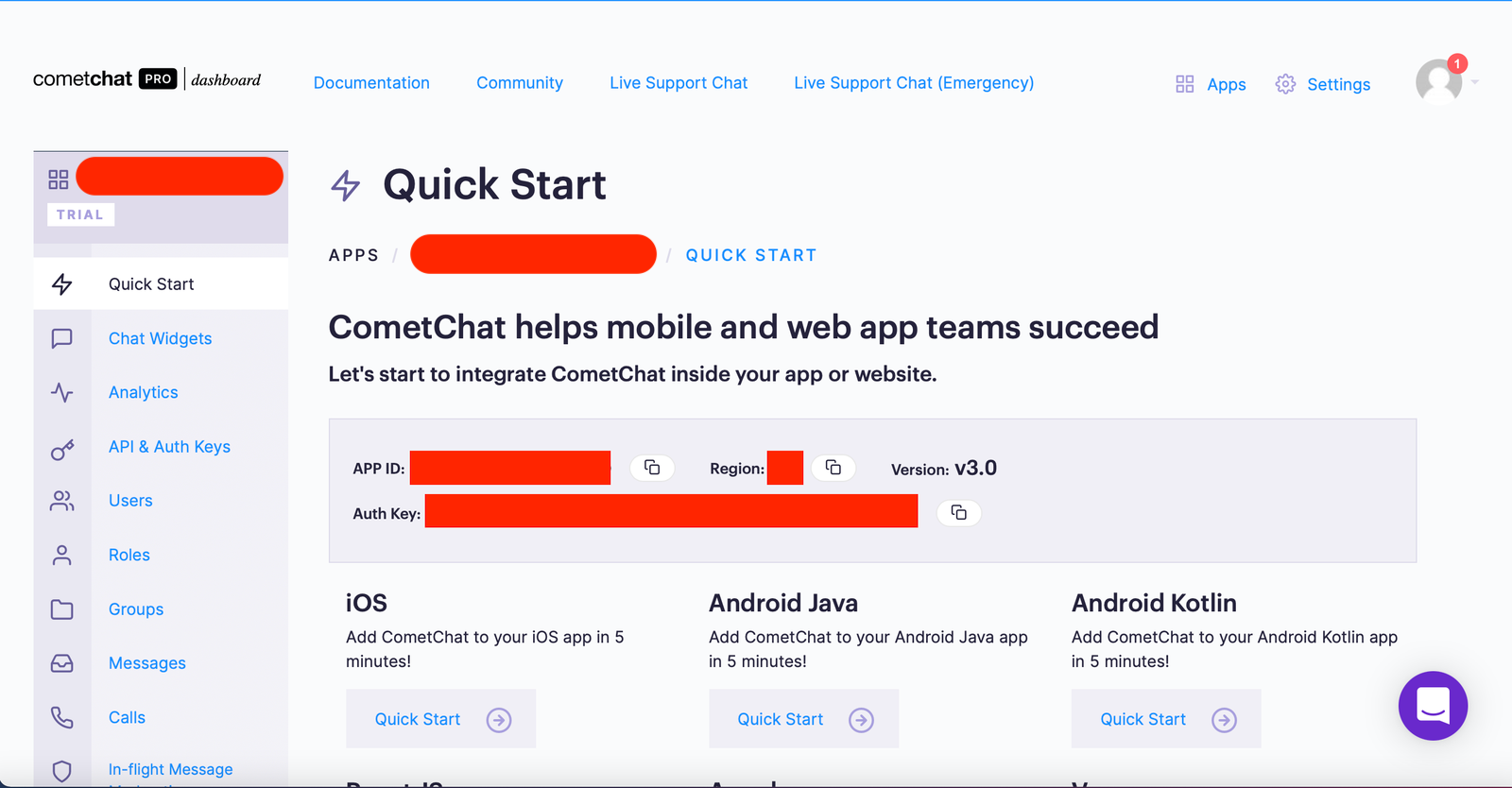
Copy the the APP_ID, REGION, and AUTH_KEY
Navigate to the Users tab, and delete all the default users (very important).
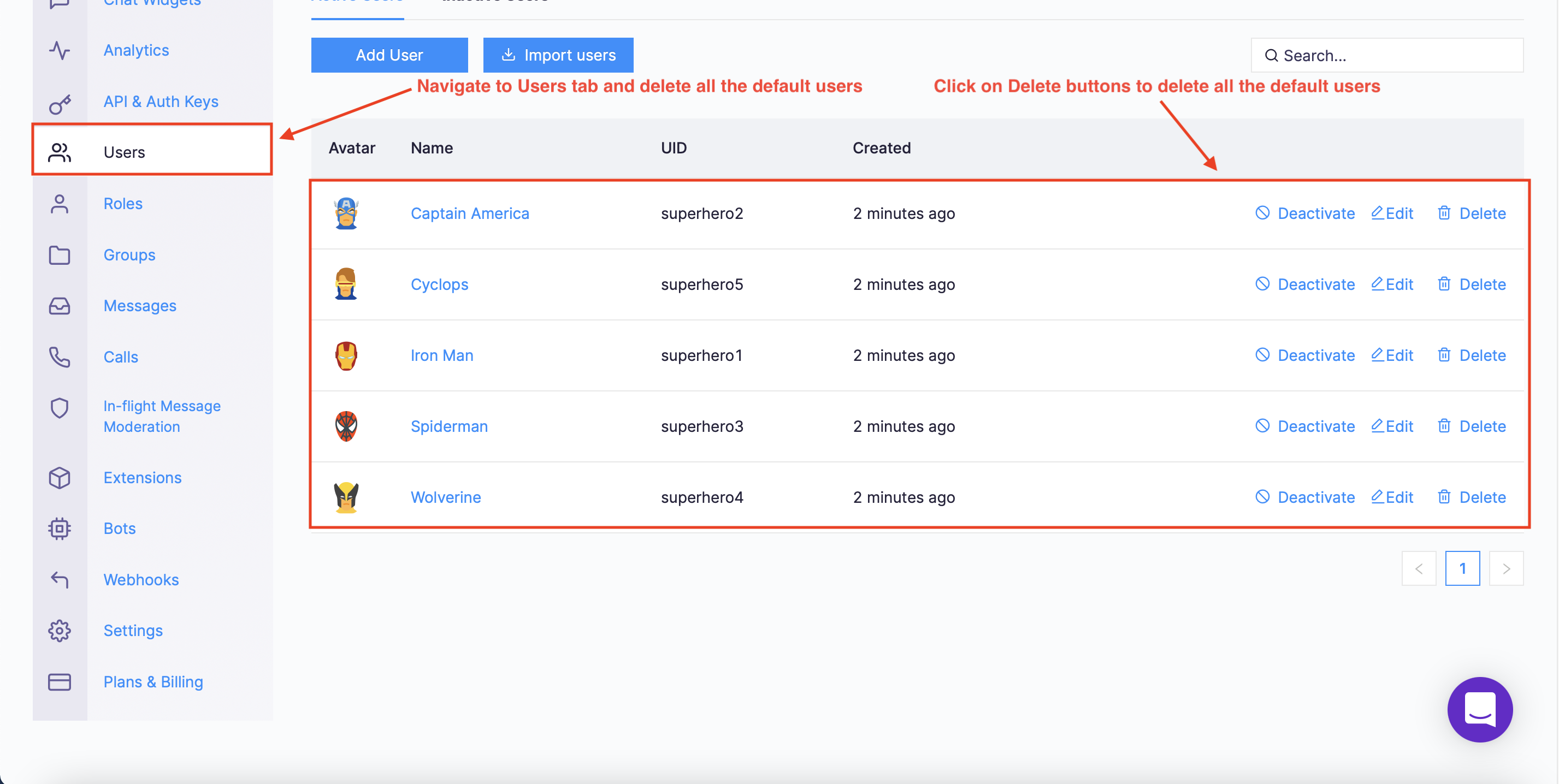
Navigate to Users tab and delete all the default users
Navigate to the Groups tab and delete all the default groups (very important).
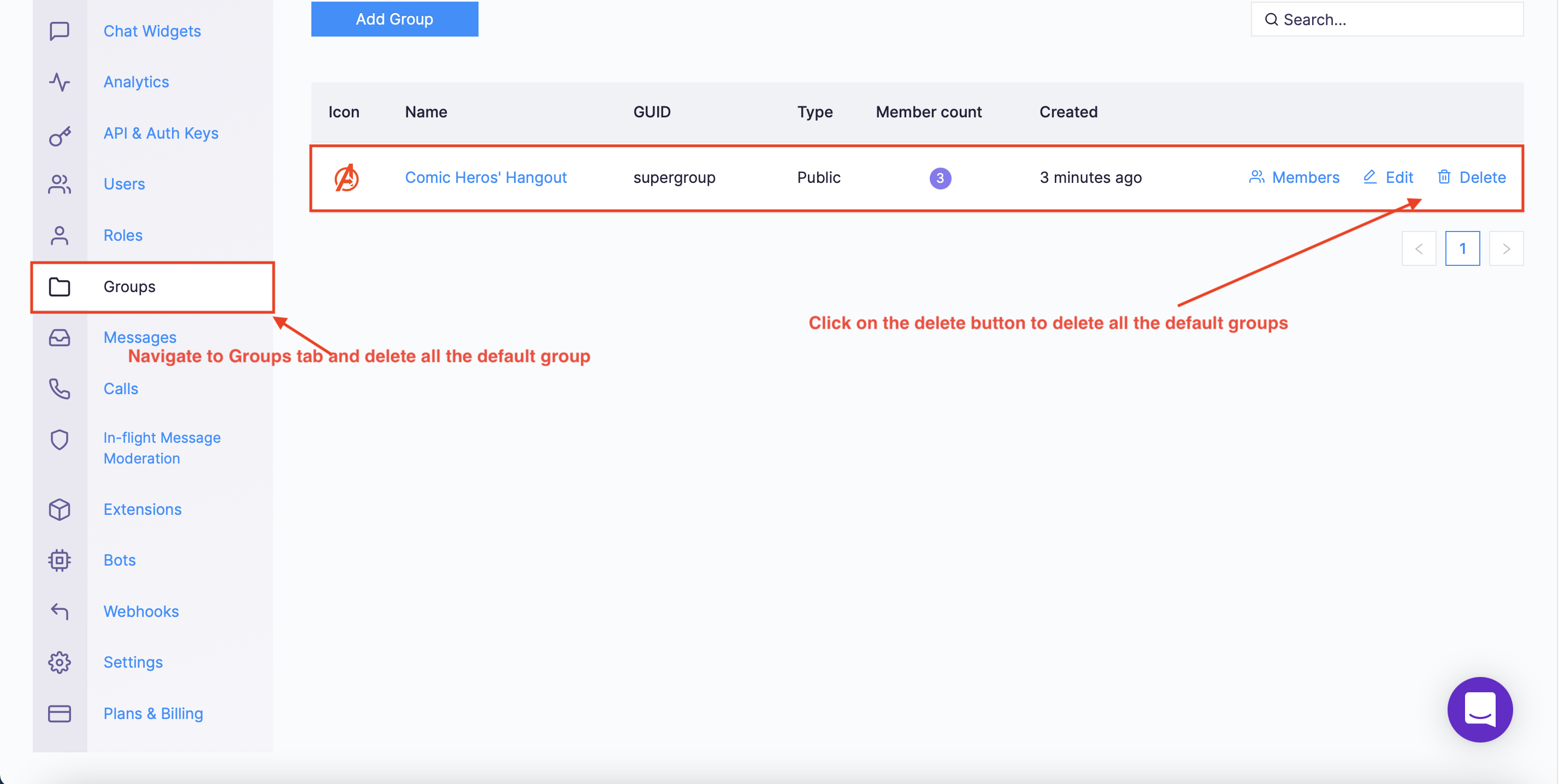
Navigate to Group tab and delete all the default groups
Create a file called **env.js** in the root folder of your project.
Import and inject your secret keys in the **env.js** file containing your CometChat in this manner.
export const cometChatConfig = { cometChatAppId: xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx, cometChatRegion: xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx, cometChatAuthKey: xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx, cometChatRestApiKey: xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx };
10. Make sure to include **env.js** in your gitIgnore file from being exposed online.
Setting Up Firebase Project
According to the requirements of the Instagram clone, you need to let users create a new account and login to the application, Firebase will be used to achieve that. Head to Firebase to create a new project and activate the email and password authentication service. This is how you do it:
To begin using Firebase, you’ll need a Gmail account. Head over to Firebase and create a new project.
Firebase
Firebase provides support for authentication using different providers. For example, Social Auth, phone numbers, as well as the standard email and password method. Since you will be using the email and password authentication method in this tutorial, you need to enable this method for the project you created in Firebase, as it is by default disabled.
Under the authentication tab for your project, click the sign-in method and you should see a list of providers currently supported by Firebase.
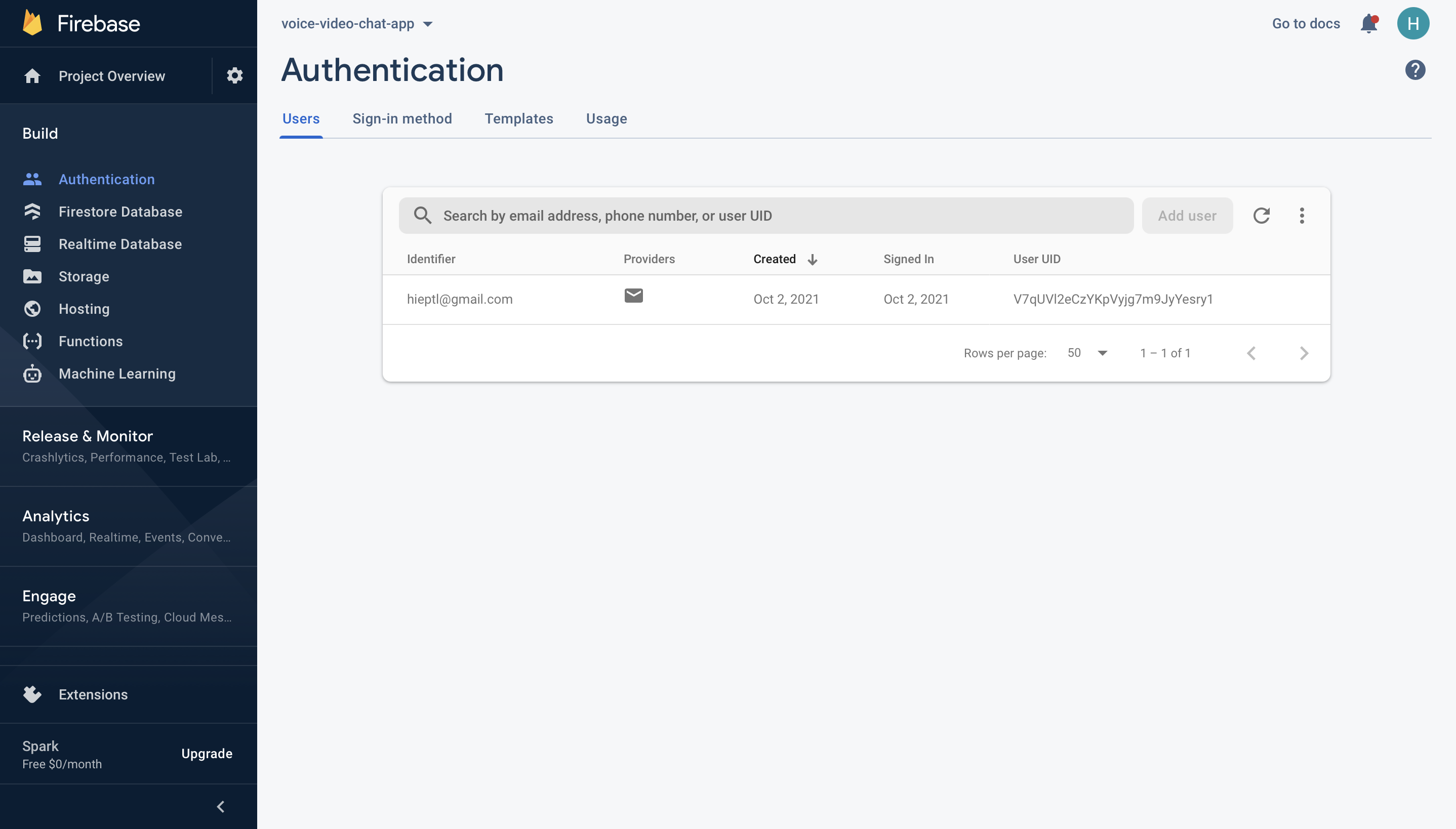
Firebase Authentication
Next, click the edit icon on the email/password provider and enable it.
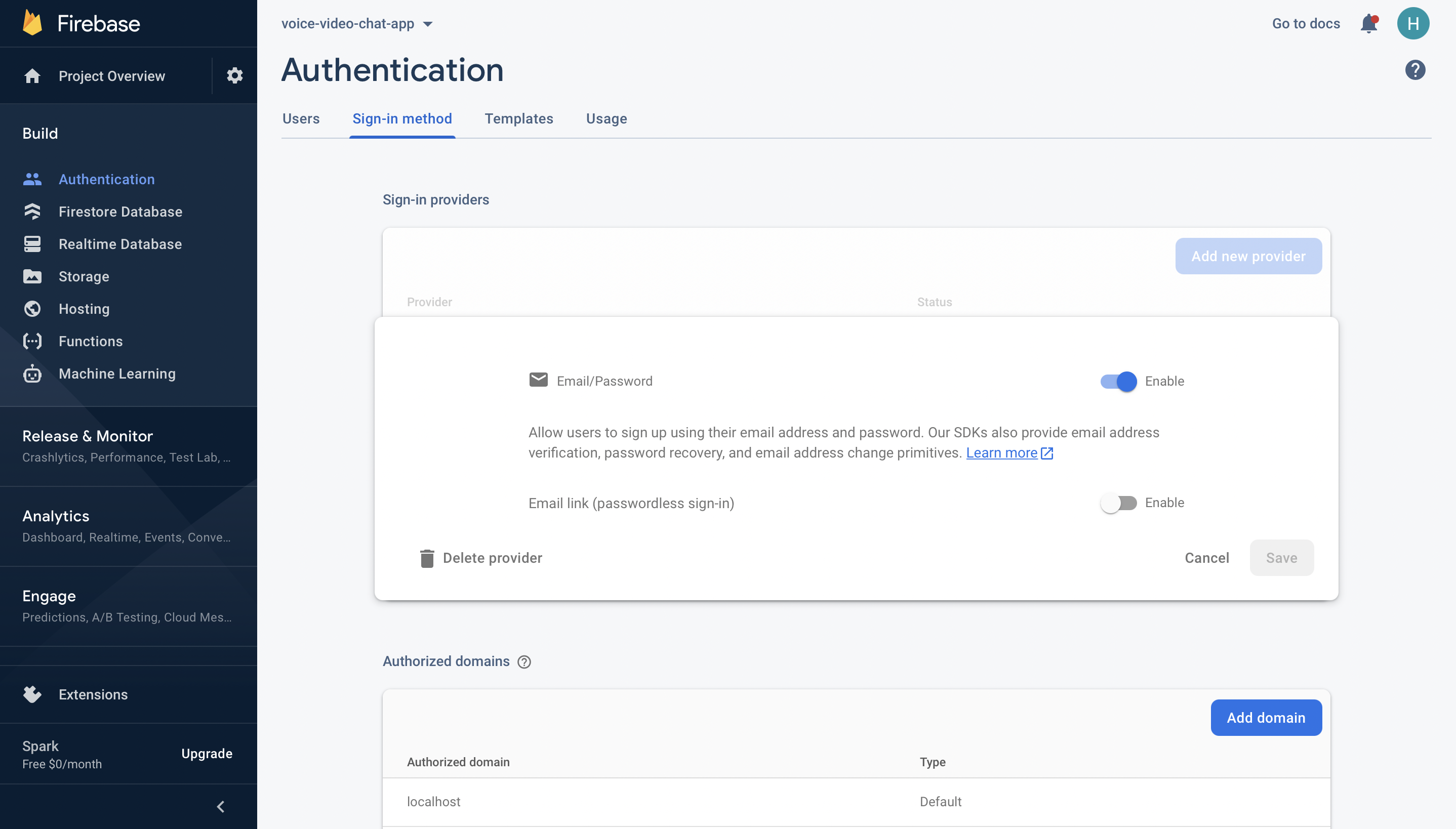
Firebase Authentication with Email and Password
Now, you need to go enable Firebase Realtime Database. We will use Firebase Realtime Database to store the information of the users in the application. Please refer to the following part for more information.
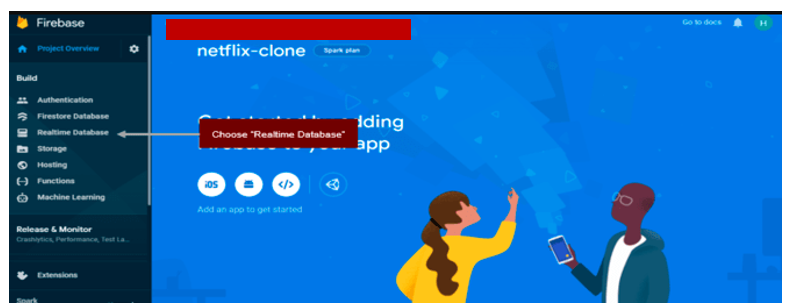
Choose “Realtime Database” option
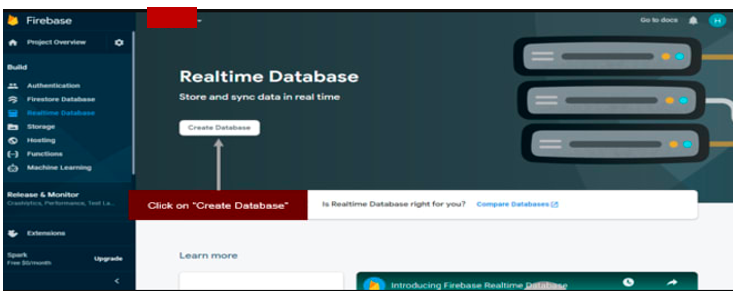
Click on “Create Database"
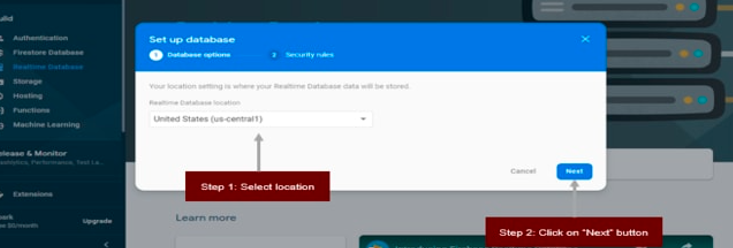
Select location where you realtime database will be stored
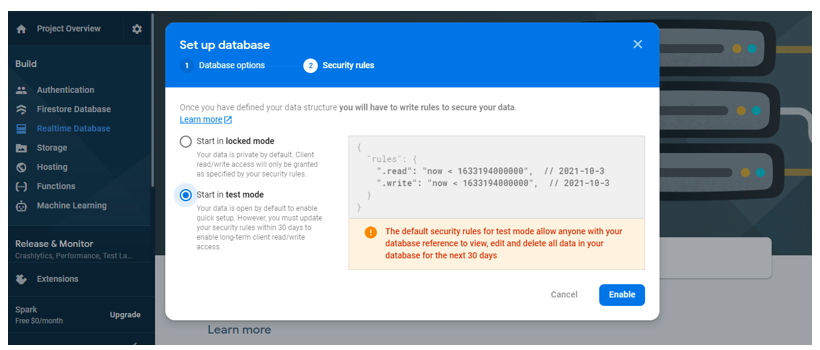
Select “Start in test mode” for the learning purpose
Please follow the guidance from Firebase. After following all steps, you will see the database URL. If you just need to update the “FIREBASE_REALTIME_DATABASE_URL” variable in your “env.js” file with that value.
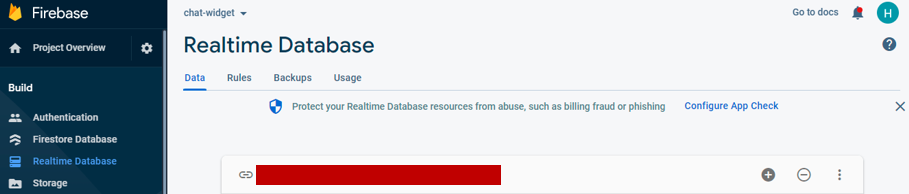
Database Url
On the other hand, your Firebase real-time database will be expired in the future. To update the rules you just need to select the “Rules” tab and update the date/time in milliseconds as you can see in the image below.
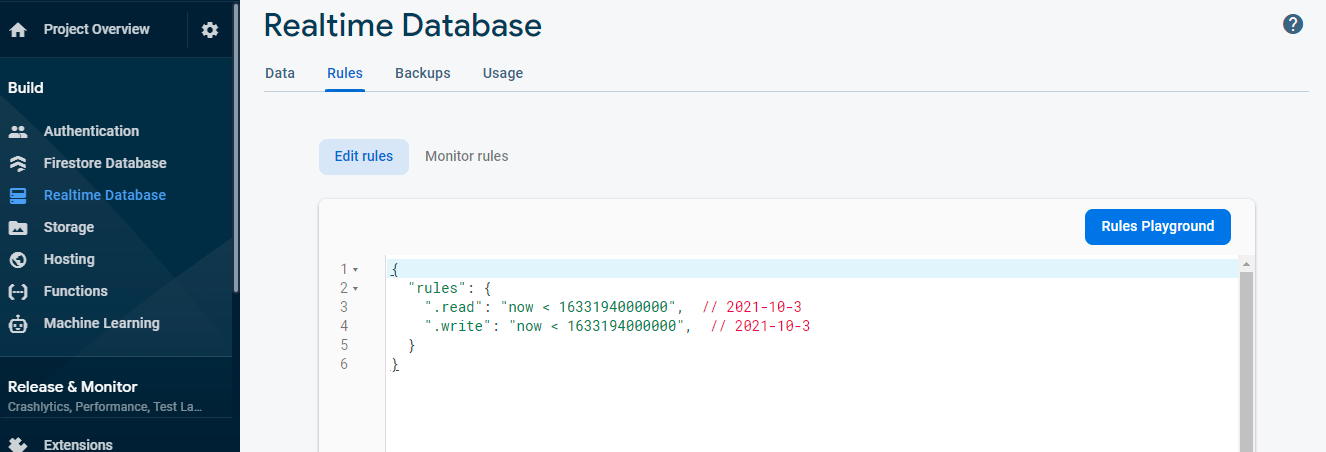
Update Firebase Realtime Database Rules
In this project, we also need to upload the post’s images, and user’s avatars. Therefore, we have to enable the Firebase Storage service, the Firebase Storage service helps us store the assets files including images, videos and so on. To enable the Firebase Storage service, please follow the below steps
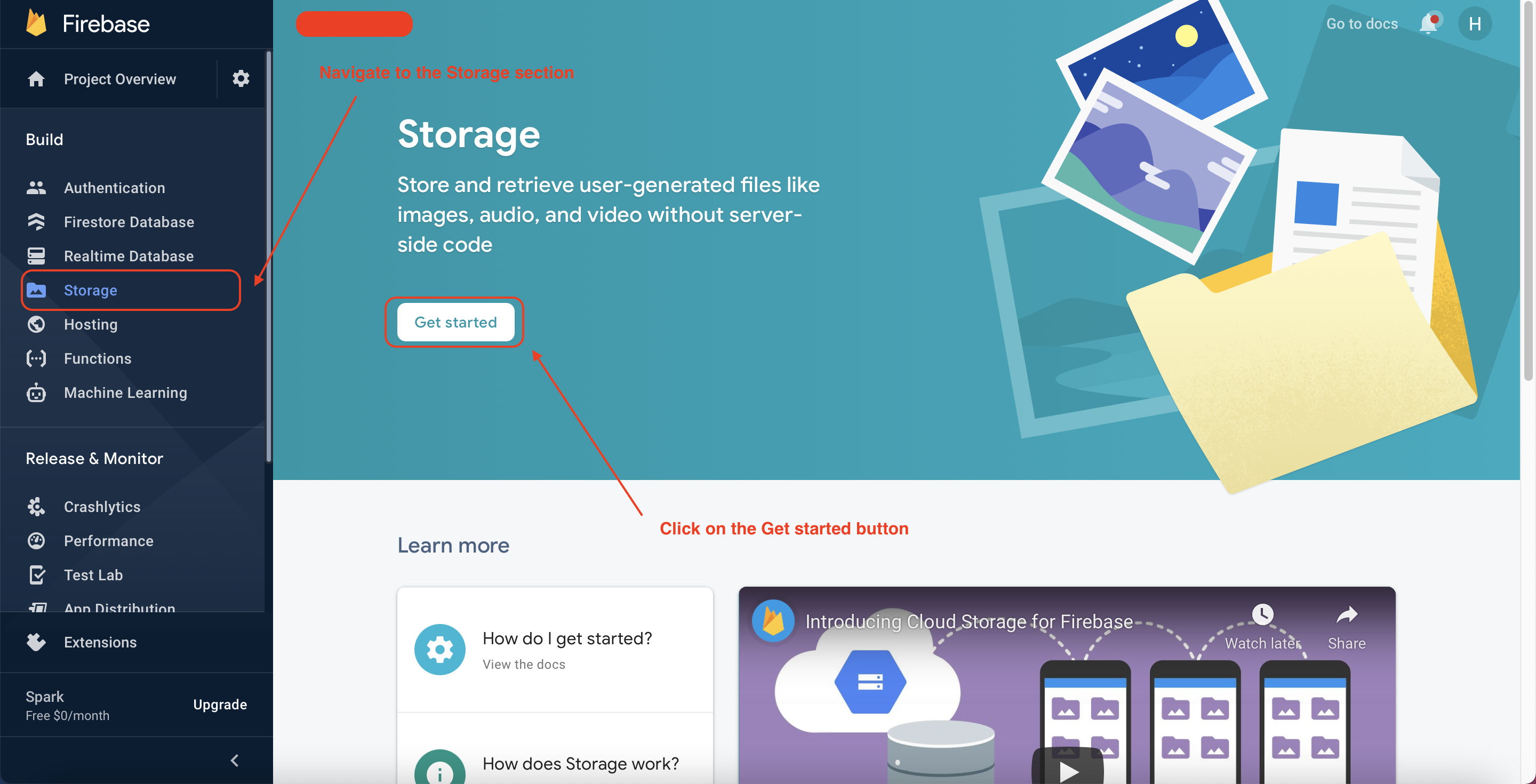
Enable Firebase Storage Service
Click on the “Next” button
Click on the “Done” button
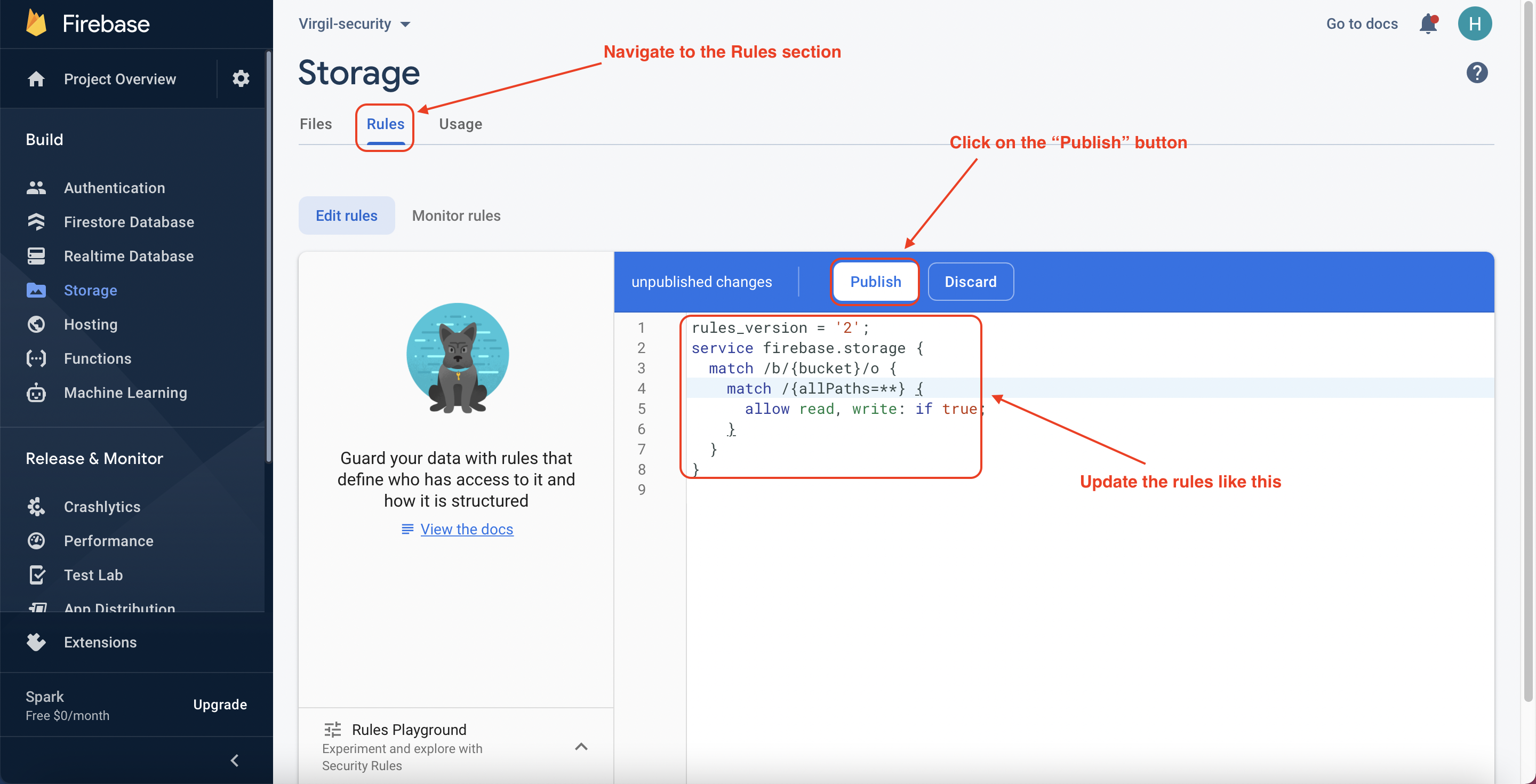
Update the rules
For the learning purposes, we need to update the rules of the Firebase Storage service. It means that everyone, who can access to the application, can upload to the Firebase storage.
Now, you need to go and register your application under your Firebase project. On the project’s overview page, select the add app option and pick web as the platform.
Firebase Dashboard
Once you’re done registering the application, you’ll be presented with a screen containing your application credentials.
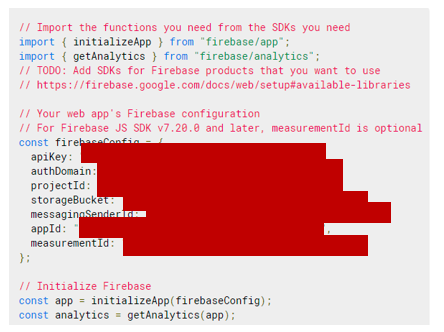
Firebase credentials
Please update your created “env.js” file with the above corresponding information. Now your “env.js” file should look like this.
As you can see in the below image, the user information contains the avatar, email, list of followers, full name, id, number of followers, and number of posts.

Data Structure - User
In this application, the end-users can upload the posts. Therefore, we need to store the post information in the Firebase Realtime Database.

Data Structure - Post
The post information contains the author information, content, id, list of likes, and number of likes. After the end-users have liked any post or followed someone, the application will save the notifications and send those notifications to the related users as you can see in the below image.
For example, Camila has liked the Anna’s posts or followed the Anna’s profile so the notifications will be sent to Anna in real-time.
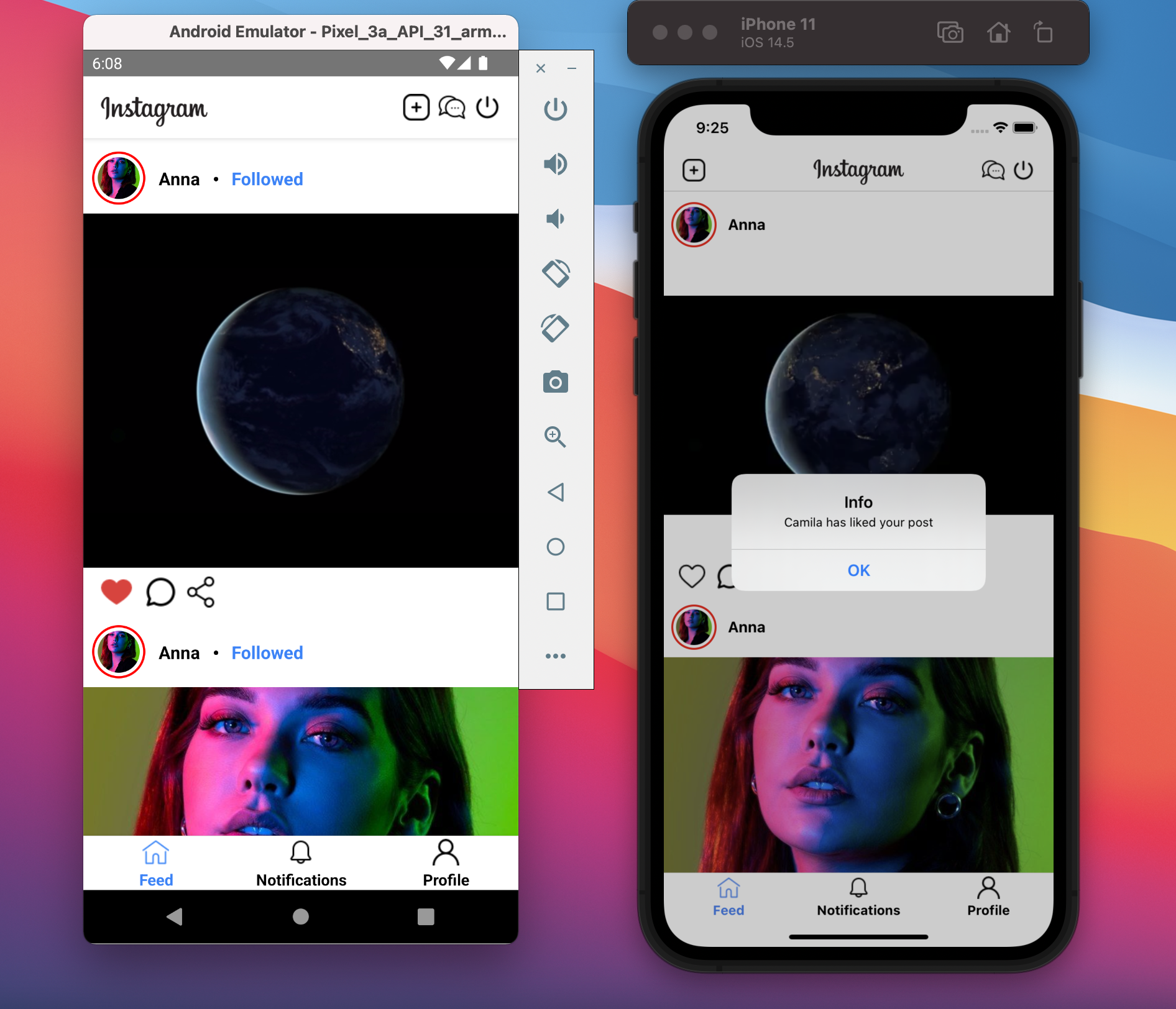
Notifications when someone has liked your posts
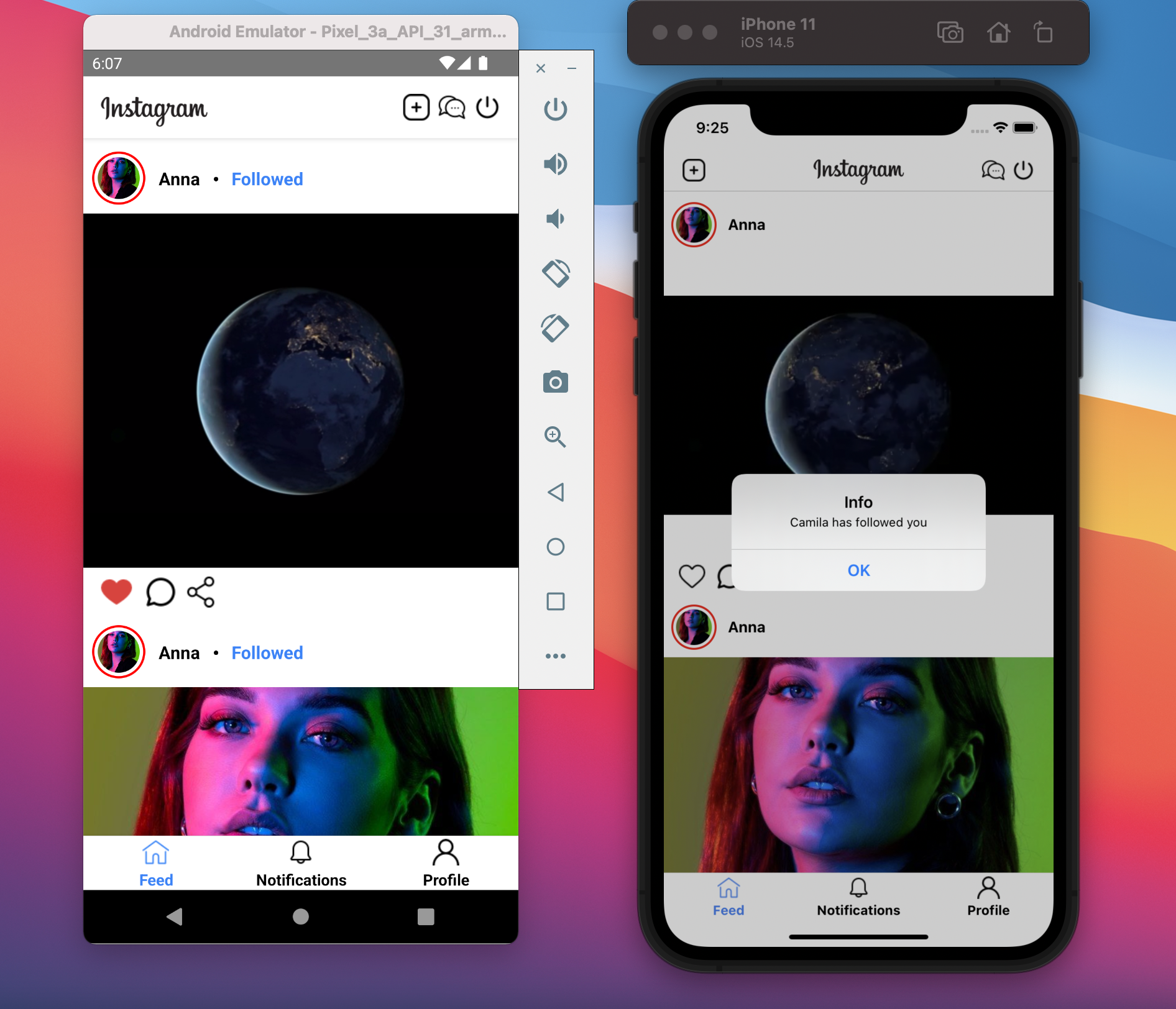
Notifications when someone has followed you
The below image demonstrates the data structure of notifications in the Firebase Realtime Database.

Data Structure - Notification
Congratulations, now that you're done with the installations, we will add the CometChat UI to our application in the next section.
Add the CometChat UI to our Application
Before we can use the CometChat Pro React Native UI kit, we need to add it in our project so that we can reference it. In this case, we are using React Native UI Kit v3.0. To do that, follow the next steps:
Step 1: Clone the CometChat React Native UI Kit Repository like so. For more information about React Native UI Kit, you can check this link.
https://github.com/cometchat-pro/cometchat-pro-react-native-ui-kit.git -b v3Step 2: Copy the cometchat-pro-react-native-ui-kit folder to your source folder.
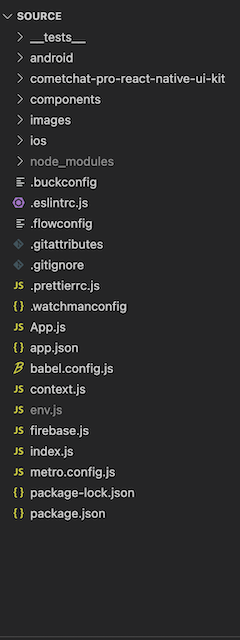
Copy the project into your source folder.
Step 3: Please check your current package.json file, if your package.json file did not have the dependencies as you can see in the peer dependencies section, please copy all the peer dependencies from package.json into your project's package.json and install them using npm install.
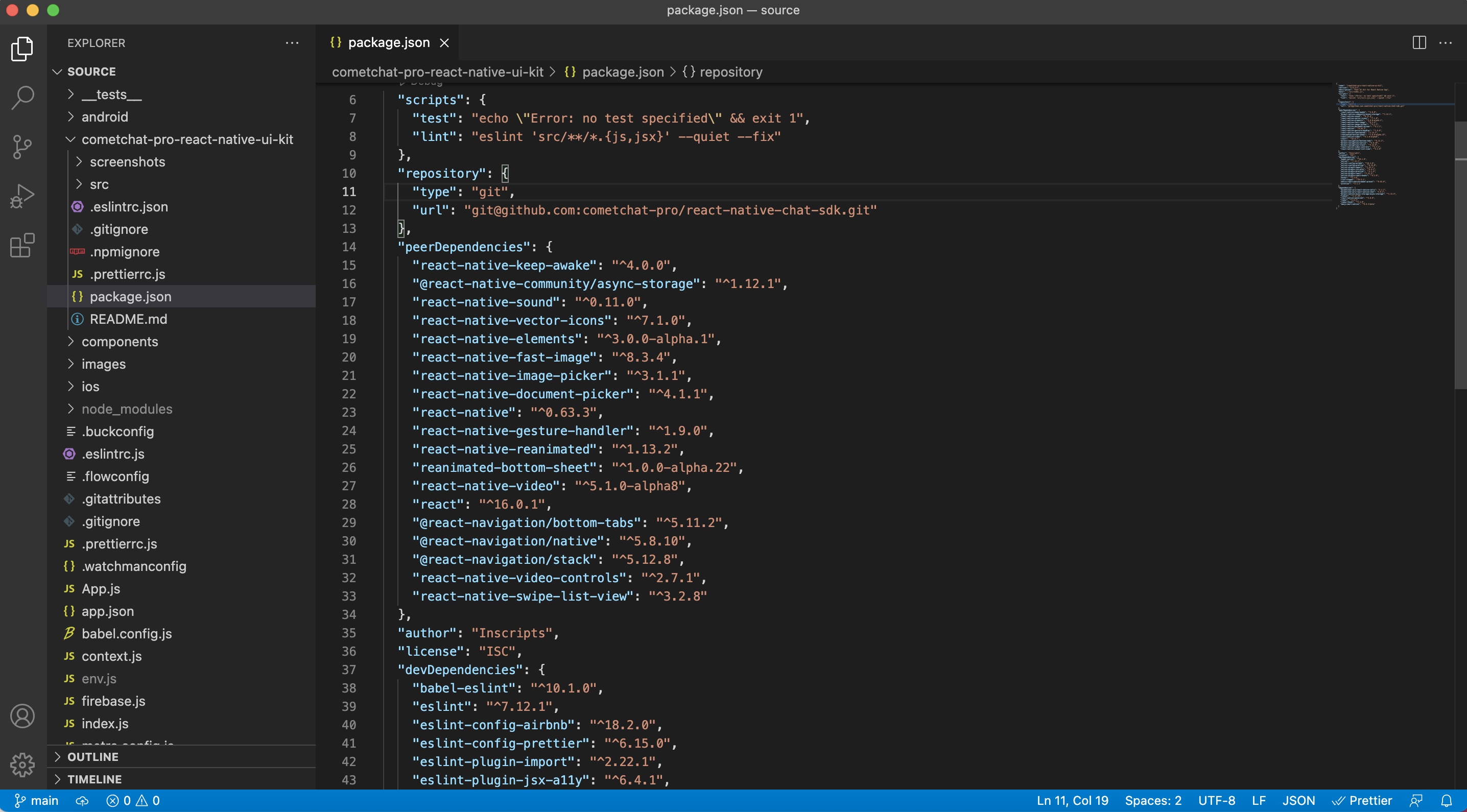
Copy all peer dependencies and install them
As soon as the installation is completed, you now have access to all the React Native UI Components. The React UI kit contains different chat UI components for different purposes as you can see in the documentation here. It includes:
1. CometChatUI
2. CometChatUserListWithMessages
3. CometChatGroupListWithMessages
4. CometChatConversationListWithMessages
5. CometChatMessages
6. CometChatUserList
7. CometChatGroupList
8. CometChatConversationList
9. CometChatAvatar.
10. CometChatUserPresence
11. CometChatBadgeCount
Project Structure - Client Side
The image below reveals the project structure. Make sure you see the folder arrangement before proceeding.
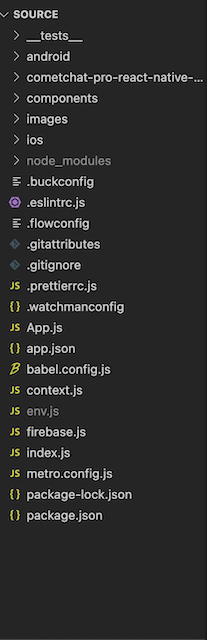
The Project Structure
components: this folder stores components that will be used in the application.
images: this folder contains images that will be used in the application such as audio icon, video icon, settings icon and so on.
env.js: this file stores configuration of the application such as Firebase and CometChat configuration.
context.js this file helps us store the state that will be shared across all components without passing down at every level. For this reason, we can avoid props drilling.
Creating React Context
In this application, we need to pass some data between the components. We can save several options to achieve that such as using state management libraries, RxJS, and so on. However, we can get in-built support from React by using the React Context API. the React Context API helps us pass data through the component tree without passing down at every level. Please create the “context.js” file inside the “src” folder. The full source code of the “context.js” file can be found here.
Initializing CometChat for the Application
The below codes initialize CometChat in your app before it spins up. The App.js file uses your CometChat API Credentials. We will get CometChat API Credentials from the .env.js file. Please do not share your secret keys on GitHub.
Actually, App.js does not contain only the above code. It also contains other business logic of the application. The full source code of App.js file can be found here.
The App.js File
The App.js file is responsible for rendering different components by the given routes. For example, it will render the login page if the user has not logged in, yet or it renders the home page if the user has signed in to the system. On the other hand, it will be used to initialize CometChat. The full source code of the App.js file can be found here.
The Login Component

The Login Component
This component is responsible for authenticating our users. It accepts the user credentials and either signs him up or in, depending on if he is new to our application. You can refer to the below steps to understand the authentication flow.
Step 1: The users input their credentials (email/password).
Step 2: The application validates the credentials.
Step 3: If the credentials are valid, the application calls the Firebase Authentication service by using those credentials.
Step 4: If the Firebase Authentication service returns the user’s aid the application continues to log in to the CometChat using the returned uid.
Step 5: If the CometChat service returns the valid response, the application calls the Firebase Realtime Database service to get the authenticated information, and then store that information in Async Storage. Therefore, when we need to get the authenticated information, we just need to get the data from Async Storage instead of calling the Firebase Realtime Database service.
See the code below and observe how our app interacts with the Firebase Authentication service, and the CometChat SDK. Please create the “login” folder inside the “components” folder, and create the “Login.js” file inside the “login” folder. The full source code can be found here.
We store the authenticated Information to the local storage for further usage such as getting that information in different places in the application, prevent the end-users come back to the login page after signing in to the application.
To login to the CometChat, we call the cometChat.login function, you can refer to the below code snippet for more information.
We will discuss the sign-up component in the following section.
The Sign Up Component

The Sign Up Component
The sign-up component will help end-users to register new accounts. This component will do two things. The first thing is to register new accounts by calling the create user API. Aside from that, it also registers new accounts on CometChat by using the CometChat SDK. Please create the “register” folder inside the “components” folder, and create the “SignUp.js” file inside it.
To create a new CometChat account, we call cometChat.createUser function. You can refer to the below code snippet below for more information.
The Bottom Navigation Component
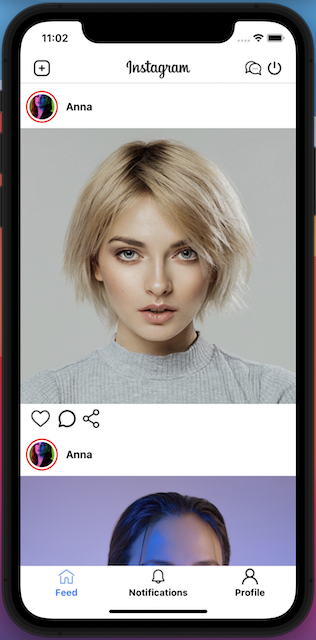
The Bottom Navigation Component
In this section, we create the bottom navigation as you can see in the above image. To create the bottom navigation, please create the “navigation” folder inside the source folder, and create the “Tabs.js” file inside it. The full source code can be found here.
In this case, we use createBottomTabNavigator(); to create the bottom navigation in our application, it is imported from the “@react-navigation/bottom-tabs”. If you run the code, you may face with some errors because we have not defined some components that are used in the bottom navigation - Home, Chat, Notifications, Profile. You can create some empty component to overcome the errors. We will discuss those components in the following sections.
The Home Component

The Home Component
The Home contains list of posts. Please create the “home” folder inside the “components” folder, and create the “Home.js” file inside it. The full source code can be found here.
The above code snippet shows that the Home component includes the Posts component. The Posts component is used to render the list of posts in the application.
The Posts Component

The Posts Component
As mentioned above, the Posts component is used to render the list of posts on the UI. It gets the data from the Firebase Realtime Database, render the data by using the FlatList component, and then pass each item in the list to the Post component. Each post is rendered by the Post component. The Post component will be discussed in the following part. Please create the “posts” folder inside the “components” folder, and create the “Posts.js” file inside it. The full source code can be found here.
As mentioned earlier, after the end-users have liked any post or followed someone profile, the notifications will be created, and the custom messages are sent to the related users. For example, Camila has liked the Anna’s posts or followed the Anna’s profile so the notifications will be sent to Anna in real-time. The CometChat services help us to send custom messages in real-time, the receivers just need to listen to those custom messages and then display the corresponding notifications.

Notifications when someone has liked your posts

Notifications when someone has followed you
You can refer to the below code snippet for more information.
To listen to the custom messages, we will write the logic code in the App component as follow.
The Post Component

The Post Component
As mentioned above, each item on the post list is rendered by using the Post component. The Post component will accept the post’s information, and the callback function that will be triggered after the end-users click on any post. Please create the “Post.js” file inside the “posts” folder. The full source code of the Post component can be found here.
The Detail Component

The Detail Component
If the end-users click on any post in the list, the users will be redirected to the Detail page, the Detail component is used to show the content of the selected post. Please create the “Detail.js” file inside the “posts” folder. The full source code can be found here.
The Create Component

The Create Component
According to the requirements, the end-users can upload the posts. To go to the Create page, the end-users click on the plus icon on the top-left corner of the header. The users can choose an image or a video from their phone, after selecting the image/video, the data will be stored in the “post” state. If the users really want to upload the post, they just need to click on the “Create Post” button. The application will upload the selected image/video to the Firebase Storage service and get the downloaded url. After that, the application calls the “buildPost” function to build the Post object and calls the Firebase Realtime Database to insert the post. Last but not least, the application also update the number of posts for the current user. Please create the “create” folder inside the “components” folder, and create the “Create.js” file inside it. The full source code can be found here.
The Profile Component
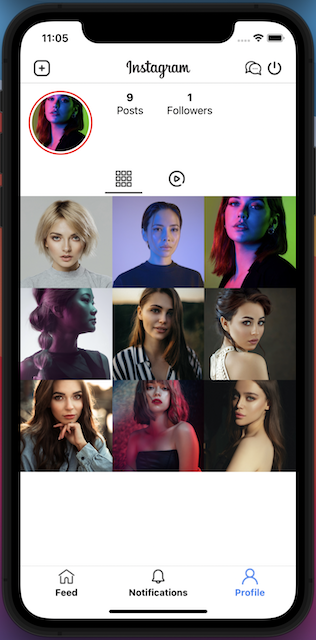
The Profile Component
To view the profile of the current user, we can click on the “Profile” option on the bottom navigation. The profile component displays the detail information of the selected user including the avatar, number of posts, number of followers, list of posts, and so on. Please create the “profile” folder in side the “components” folder, and create the “Profile.js” file inside it. The full source code can be found here.
As you can see in the above code snippet, the Profile component includes the Header component, Action component and reuse the Posts component that we have created before. The Header component and the Action component will be discussed in the following sections.
The Header Component - Profile

The Header Component - Profile
The Header component displays the user’s avatar, number of followers, number of posts, and the follow button. Please create the “Header.js” file inside the “profile” component. The full source code can be found here.
The Actions Component - Profile

The Actions Component - Profile
If we view someone’s profile, we can view the list of images and list of videos by clicking on the icons of the Actions component. If we click on the “grid” icon, we can view the list of of images and vice versa. Please create the “Actions.js” file inside the “profile” folder. The full source code can be found here.
The Profile Post Component

The Profile Post Component
Each item in the profile page is rendered by using the ProfilePost component. In the profile tab, we render the list as grid as you can see in the above image. Please create the “ProfilePost.js” file inside the “posts” folder. The full source code can be found here.
The Notifications Component
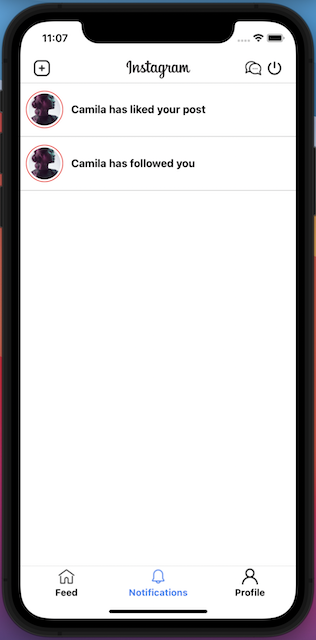
The Notification Component
The Notifications component displays the list of notifications such as who liked your posts, who followed your profile, and so on. The Notifications component interacts with the Firebase Realtime Database to get the list of notifications, and it listen to the changes in the notifications data in real-time. Please create the “notification” folder, and create the “Notifications.js” file inside it. The full source code can be found here.
The Notification Component

The Notification Component
Each item in the notifications will be rendered by using the Notification component. After the parent component has interacted with the Firebase Realtime Database to get the notifications data, it will show that data on the UI by using the map function, each item in the list will be passed to the Notification component via props. Please create the “Notification.js” file inside the “notification” folder. The full source code can be found here.
The Chat Component
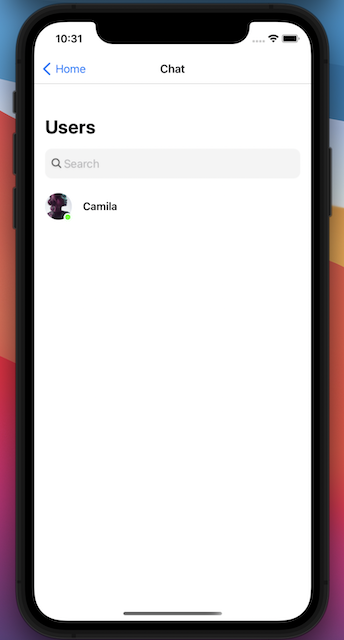
The User List
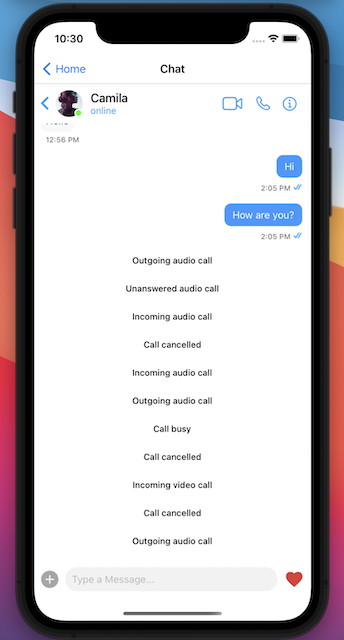
The Chat Screen
The Chat component will use the CometChatUserListWithMessages, and CometChatMessages components to achieve the chat feature. We import those components from the CometChat React Native UI Kit that we have added it to our project in the previous section. Please create the “chat” folder inside the “components” folder, and create the “Chat.js” file inside it. The full source code can be found here.
The Logout Feature
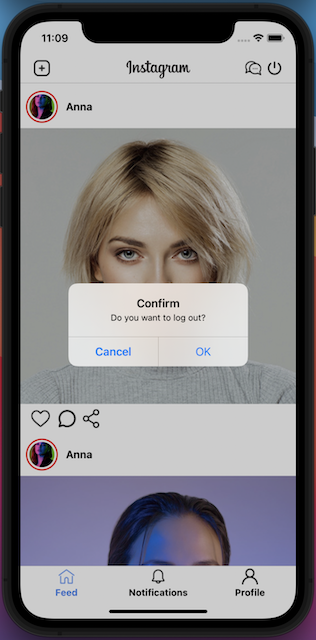
The Logout Feature
To logout from the application, the end-users click on the power button, a confirmation dialog will be displayed, if the end-users would like to sign out, the users just need to click on the “Ok” button. After that, the application will do some clean-up actions before redirecting the users to the home page. Please refer to the below code snippet for more information.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, we have done an amazing job in developing an Instagram clone by leveraging React Native, Firebase, and CometChat React Native UI Kit. You’ve been introduced to the chemistry behind Instagram and how the CometChat makes the Instagram clone buildable.
You have seen how to build most of the chat functionalities such as real-time messaging using CometChat. I hope you enjoyed this tutorial and that you were able to successfully add mentions into your React chat app. Jump into the comments and let me know your experience.

Hiep Le
CometChat